Hello, welcome to Guangdong Heyi Hardware Products Co.,Ltd. website!
Hello, welcome to Guangdong Heyi Hardware Products Co.,Ltd. website!
Strength
The material must be able to withstand the forces applied in the application scenario without bending, breaking, shattering or deforming.
Hardness

Harder materials are generally more scratch resistant, durable and resistant to tears and indentations.
Flexibility
The ability of the material to absorb forces, bend in different directions and return to its original state.
Forming performance
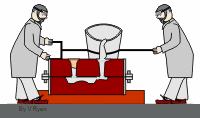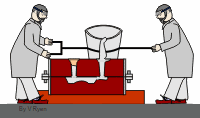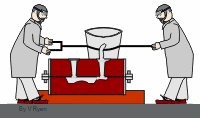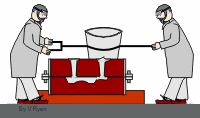
The persimmon is soft enough to be squeezed but it is finished when it is squeezed. At the other end of the spectrum, diamonds are too hard to be used for processing. Diamonds can be used for other things.
Ductility

The ability to deform under force in the length direction. The rubber band is very elastic. Material-wise thermoplastic elastomers generally have good ductility.
Tensile strength
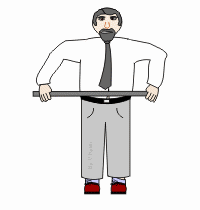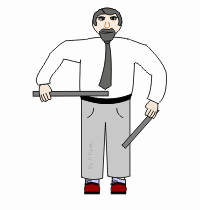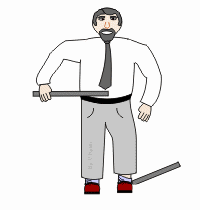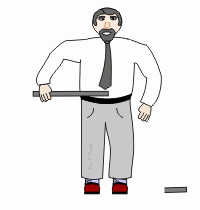
The ability to deform before fracture or breakage occurs.
Ductility
The ability of a material to change shape in all directions without cracking is a test of the material's ability to reshape itself.
Resilience

The material is impact resistant and will not break or shatter with a sudden knock. 。
Electrical conductivity

This needs no further comment from the editor. Under normal circumstances, materials with good electrical conductivity also conduct heat well.
4000-115-666
Email:mojugang@gdheyi.cn
Address:No. 8, Xinwei North Lane, Fugang, Qingxi,
Dongguan City, Guangdong Province
 Mobile website
Mobile website
 Follow the public
Follow the public